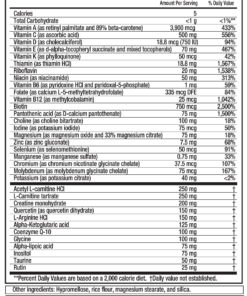
GLYCINE
Glycine in EnergyNeeds®
 Glycine is added in order to conjugate and remove (‘detoxify”) unwanted compounds such as metabolic intermediates and environmental chemicals. Side effects are unexpected.
Glycine is added in order to conjugate and remove (‘detoxify”) unwanted compounds such as metabolic intermediates and environmental chemicals. Side effects are unexpected.
The Details
What Is Glycine?
Glycine is a nonessential amino acid in that it can be made by our bodies.
What Does Glycine Do?
Glycine is one of the 20 plus amino acids that comprise all proteins. It is the smallest, and simplest, amino acid, and is particularly abundant in collagen. Glycine has an important function as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Glycine is also a building block of multiple compounds made by the body, including the natural antioxidant, glutathione, as well as creatine and heme. Glycine also regulates immune function, including the synthesis of cytokines by altering the intracellular calcium levels.
What Does A Glycine Deficiency Appear As?
Since our bodies can synthesize glycine and it is present in almost all dietary proteins, deficiency is rare.
What About Glycine‘s Use in Disease?
Glycine is used by metabolic specialists to conjugate a variety of toxic compounds, and hence facilitate their removal. Glycine is sometimes supplemented in treating patients with cardiovascular diseases, several inflammatory diseases, obesity, diabetes and some cancers. Glycine also is sometimes used to enhance the quality of sleep and to reduce fatigue.
What Are the Common and/or Important Side Effects of Glycine?
Glycine is present in all proteins, and is generally recognized as safe (GRAS-status). In Dr. Boles’ experience, glycine in dosages as high as 10 grams a day is well tolerated in individuals.
Is There Any Laboratory Testing for Glycine Deficiency?
Laboratory testing can reveal the presence of a deficiency of this nutrient, but is generally not likely to have clinically utility.
Order EnergyNeeds® Today
Formulations