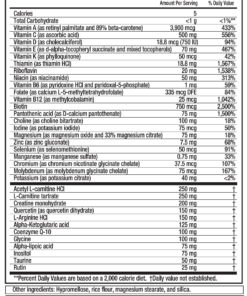
Pantothenic acid (also known as vitamin B5 or pantothenate)
Pantothenic acid in EnergyNeeds®
 Pantothenic acid is added in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of pantothenic acid in energy metabolism. Furthermore, the dosing of pantothenic acid in EnergyNeeds® is high (but not extreme) in an attempt to increase complex I activity and CoA levels, which in turn might help to facilitate a wide range of metabolic processes in the body. Side effects are unexpected.
Pantothenic acid is added in order to provide a wide basis of nutrition, especially given the important role of pantothenic acid in energy metabolism. Furthermore, the dosing of pantothenic acid in EnergyNeeds® is high (but not extreme) in an attempt to increase complex I activity and CoA levels, which in turn might help to facilitate a wide range of metabolic processes in the body. Side effects are unexpected.
The Details
What Is Pantothenic acid?
Pantothenic acid, also known as vitamin B5, is one of the eight B-complex vitamins. Pantothenic acid cannot be manufactured by humans and is thus a true vitamin, obtained exclusively from the diet.
What Does Pantothenic acid Do?
Pantothenic acid is an enzyme cofactor, which means that it is a necessary component for enzyme function. Furthermore, coenzyme A (CoA) is synthesized from pantothenic acid. CoA is itself a cofactor in a wide range of enzymes in energy metabolism, including in carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism, as well as in the Krebs cycle. CoA is also an important cofactor for enzymes in the biosynthesis fatty acids, cholesterol, and acetylcholine, among multiple other compounds. Pantothenic acid is also a cofactor of the acyl-carrier protein associated with complex I of the electron transport chain.
What Does a Pantothenic acid Deficiency Appear As?
Pantothenic acid deficiency is rare today outside of cases of extreme malnutrition or substantial GI malabsorption such as chronic diarrhea. Symptoms can include acne, fatigue, depression, irritability, insomnia, abdominal pain, vomiting, burning and tingling feet, muscle cramps, and frequent upper respiratory infections.
What About Pantothenic acid’s Use in Disease?
Pantothenic acid is sometimes recommended for a variety of uses, including acne, adrenal insufficiency, aging, alcoholism, allergies, anxiety, athletic performance, asthma, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder, autism, burning feet syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome, celiac disease, chronic fatigue syndrome, colitis, conjunctivitis, convulsions, cystitis, dandruff, depression, diabetic nerve pain, dizziness, growth deficiency, immune dysfunction, infections (frequent), insomnia, hair loss or greying, headache, heart failure, hyperactivity, low blood sugar, irritability, low blood pressure, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, muscular cramps, nerve pain, obesity, osteoarthritis, Parkinson disease, premenstrual syndrome, prostate enlargement, respiratory disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, salicylate toxicity, shingles, skin disorders, tongue infections, wound healing, and yeast infections.
What Are the Common and/or Important Side Effects of Pantothenic acid?
Pantothenic acid is a water-soluble vitamin and thus considered to be generally non-toxic. Doses as high as 10 grams are frequently given for acne, whereas nausea can occur, but is generally otherwise well tolerated.
Is There Any Laboratory Testing for Pantothenic acid Deficiency?
Laboratory testing can reveal the presence of a deficiency of this nutrient, but is generally not likely to have clinically utility.
Order EnergyNeeds® Today
Formulations